Scouts TT Goes Solar
Introduction
Scouts Go Solar is a collaboration focused on utilising the sun as a main source of natural, renewable energy. This programme allows members of ScoutsTT to not only learn about, but also implement daily best practices in living greener by using sunlight as a sustainable resource. This programme is meant to encourage members to achieve their Scouts Go Solar badge through the ‘learning by doing ’method but it more importantly aids the transformation of members into active citizens who are able to create change in our culture of energy usage.
This programme involves 4 sections:
- Sun is Life
- Impacts of the Sun on Health and Environment
- Use of Solar Energy
- Go Solar!
Each section takes a step further from knowledge into application. Each gives its own information and relevant activities and would have different requirements to complete in earning this badge. You are expected to take videos and pictures of yourself completing of the activities to include in your report. Send them to your leaders to record progress made and share them with us on our social media platforms.
Being Safe
- Wash your hands after each activity, practice social distancing and wear masks while in public.
- Don’t look directly at the sun
- Don’t drink water unless you are sure that it is safe to do so
- Be careful with mirrors and magnifying glasses in direct sunlight. Ensure that they are not left unattended. Remember to cover after using them.
- Ensure that you are adequately protected from the effects of sun exposure by either wearing sunscreen or covering up with clothing.
- Always test how hot something is before grabbing it.
- Recycle or reuse materials in activities as much as possible.
How to earn the Badge?
Work with your parent, guardian or leader to develop a plan complete the activities required to earn the badge. Youth members can save all of the activity reports and share them with their leader at the end for approval. Once the leader is satisfied that the youth member has done enough, they can issue the badge certificate which can be used to purchase the badge.
Badge Requirements
Cubs
- Section A – Complete 2 activities in this section
- Section B – Complete 2 activities in this section
- Section C – Complete 1 activity in this section
- Section D – Complete 1 activity in this section
Scouts
- Section A – Complete 2 activities in this section
- Section B – Complete 2 activities in this section
- Section C – Complete 2 activities in this section
- Section D – Complete 1 activities in this section
Venture Scouts / Rovers
- Section A – Complete 3 activities in this section
- Section B – Complete 3 activities in this section
- Section C – Complete 2 activities in this section
- Section D – Complete 2 activities in this section
Activity Key
- CS – Cub Scouts
- S – Scouts
- VS/R – Venture Scouts and Rovers
- ALL – All Sections
Section A – Sun is Life
Chasing Light – CS, S
Discover how a plant turns/grows towards the light.
- Visit a field with flowers and observe it or take pictures of it at different times of the day. Alternatively, you can also grow your own flower and observe it, or grow a bean by putting the seedling in a box.
Items:
- Cardboard box
- Cardboard
- Tape/glue
- Bean’s seedling
- Knife/scissors
- Camera for time-lapse photography (phone etc.)
- Cut a 1 cm x 1 cm hole on one side of the box
- Make sure that there is no light coming into the box except from the hole you cut.
- Observe how your plant is growing after a few days
Shadow Thief – CS
- Somebody has to be the Shadow Thief and tries to catch the shadow of the fleeing children with her/his feet.
- Once he or she catches someone’s shadow, the person who is caught loses her/his shadow and becomes the next Shadow Thief.
Solar Art – ALL
Always wear sunglasses for this experiment!
Wear ultra-strong sunglasses or sunglasses with an extra layer or UV absorbing black plastic. You may use car window tint and glue it on the sunglasses.
- Try to focus the sunlight with a magnifying glass or curved mirror on a wooden plank so that the wood gets slightly burned.
- You can make a drawing or write a text or your name. To make it easier you can first draw lines with a pencil (not pen) on the wood.
- When you’re done, put the lenses back in a closed container. If left in the sunlight, it may cause a fire (If needed, this is a good way to start a fire, using the help of the sun and a lens)
- For this activity, never leave children without supervision and keep a pail of water close by in case of emergency.
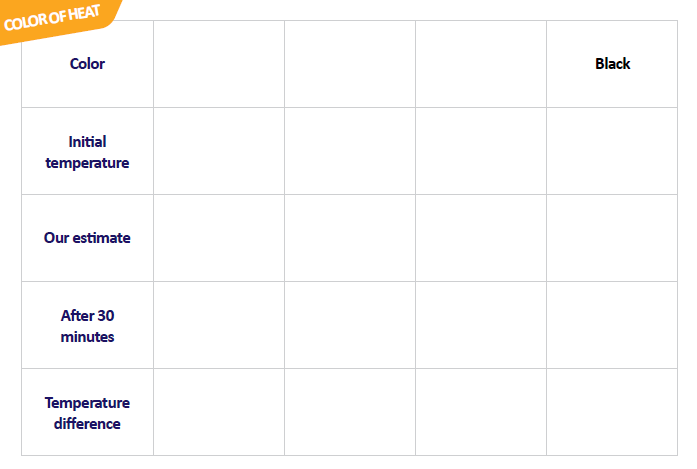
Colours of Solar Energy – CS, S
PET Bottle – made of polyethylene terephthalate can be recycled and used to manufacture new bottles and containers
Items:
- PET bottles
- Different colours
- Water
- Paint small PET plastic bottles in different colours, at least one black, one white. Alternatively, you can place the bottles in different coloured plastic bags. Fill them with water and sort them, how you think they would be, from coolest to hottest.
- Put the bottles in direct sunlight and after 30 minutes, sort them based on how warm they feel, from coolest to hottest. What did you observe?
Advanced: Measure the temperature of different material surfaces in direct sunlight (mirror glass, dusty and clean glass, etc). What can you observe and what does it mean for the use of solar energy?
Sundial – ALL
Build a sundial in your yard to help you tell the time.
What you need – A straight stick at least 12 inches long, one large stone and approximately 12 other smaller stones of similar size. If this is being done on a paved surface, you can stick a pencil through the centre of a paper plate and use some modelling clay or flour dough to hold it upright. Be sure to add some stones on top of the plate to keep it weighed down.
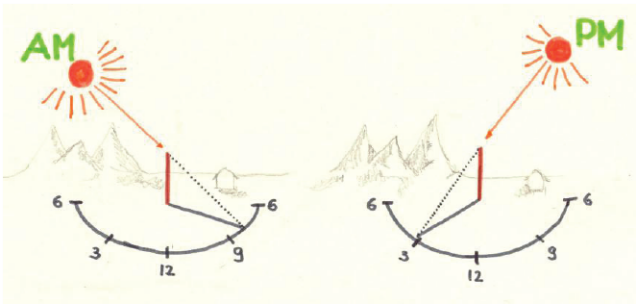
Method
Take your straight stick to a spot in your yard or a park that receives sunlight throughout the entire day. Stick it in the dirt so that it stands straight up or alternatively place the pencil and plate down and add stones to prevent it from flying away.
Once your stick is secured, leave it alone and visit it at precisely 12 noon. Notice where the end of the stick’s shadow is and place the largest stone on the floor to mark the spot. Visit the sundial at each hour and place a stone to mark the end of the shadow until sunset.
Wake up early the next morning and do the same from the first hour of sunlight and continue until noon. Your sundial should now be fully calibrated so that you should be able to accurately tell the time by looking at where the shadow is during the day.
Test this out during the week to make sure that your sundial is accurate.
Advanced – Investigate if the direction of the sun’s shadow will change during the year and explain why it might happen.
Solar and other energy sources – VS/R
- Research what we use to generate electricity in Trinidad and Tobago and where our power plants are located. Try to find out how much energy our country uses and how much solar energy we receive.
- You need to find out:
- the amount of energy the sun releases onto a surface the size of Trinidad and Tobago in a year (You can refer to the example at www.gaisma.com)
- the amount of electricity that is generated in Trinidad and Tobago in a year.
- Find out about the most convenient ways to increase the sources of renewable energy in your country.
- What is the most suitable renewable energy for your area and why?
- Present the results of your research to your team or family.
Solar Compass – ALL
- Hold an analogue watch horizontally and point the hour hand in the direction of the sun.
- Divide into half the angle between the hour hand and 12 o’clock. If you are on the northern hemisphere, this direction shows you south, if you are on the southern hemisphere, it shows you the north. (Tip: We are in the northern hemisphere!)
Advanced: Discuss how this compass works.
Section B – Impacts of the Sun on Health and Environment
Ozone and Sunburn – ALL
Identify if the Caribbean is under the ozone layer and how this affects your life.
Research how ozone is formed.
Do you know your skin type? Identify your skin type and learn how to take care of your skin to protect it from sunlight.
Advanced: Why is the ozone good and bad for us in the same time?
Don’t get a sunburn – CS
- One child is the sun and tries to catch the other kids.
- If a child gets caught, it gets sunburn and becomes a sun as well.
- The children can use sun protection in the form of a ball (you can decorate it). The child with the ball cannot be caught.
- The game goes on for as long as it takes for the sun to catch all the humans.
How to treat a sunstroke – S, VS/R
Go online and research:
- Ways to recognize and treat sunstroke.
- How is it different from a heatstroke?
- Precautions to take to prevent a sun/heatstroke.
When you are done, create a short video explaining what you have found and share it with your leader.
Sun and Weather – S, VS/R
Investigate why Trinidad and Tobago experiences a wet and a dry season and what role the sun plays in this cycle.
Find out the following:
- Which is the wettest month of the year in our country.
- Which is the driest month of the year in our country.
- Which is normally the hottest month of the year.
- Which months do the dry season and wet season normally begin.
Share your answers with members of your group and see if anyone found and different answers
Advanced – Try to figure out where the sun is in relation to the earth for each of these months.
UV Rays and SPF – S, VS/R
Visit a pharmacy or cosmetics store that sells sunscreen.
Compare the different sun care products and the SPF values that they have listed.
Do the labels mention the SPF for both UVA and UVB rays?
Calculate how much time you can stay in the sun with no protection and different SPF levels.
What effects have the two different UV rays on your skin? What is the best protection for your skin?
Investigating the greenhouse effect – ALL
The greenhouse effect happens when light from the sun passes through the atmosphere but gets changed by some of the molecules that it meets. Once it gets changed, it remains trapped within the atmosphere and the light and heat remain. This experiment shows how much of an impact it can have on warming our planet.
What you need – two identical bowls, clear plastic wrap or a clear glass plate that is able to cover one of the bowls without leaving any room for air to pass and some ice blocks.
Method:
Place 10 blocks of ice in each of the bowls. Try to make sure that the blocks of ice are the same size.
Cover one of the bowls with plastic wrap or the glass plate making sure that there is no room for air to escape. This will represent our atmosphere. Leave the other bowl completely open
Place both bowls outside in the sun and record the time. Check on both bowls regularly and note in which of the bowls the ice melts first. Record the time and keep checking to see when the ice melts in the second bowl.
Compare your results to other members of your group and finally answer the question, which bowl ran out of ice first?
Section C – Use of Solar Energy
Sun one day – everyday – ALL
Try to identify everything around you that sunlight affects.
Are there more possibilities of using sunlight or solar energy in your life?
Can you live one day in the coming week by relying only on solar energy?
What if you had to do so for your whole life?
Discuss these answers with your family and figure out if you can make more use of the sun in your home.
Solar box cooker (using cardboard, foil) – S, VS/R
Build your own solar cooker using the template below
You can follow the instructions below or research and use your own method.
Items:
- Dark pot
- Clear plastic
- Cardboard
- Foil
- Box cooker template
- Create a box cooker using the template provided. Use cardboard to create the shape of the template and coat it with foil.
- Put your food into a dark-coloured pot with a dark-coloured or clear lid.
- Place the pot inside a plastic bag or other clear enclosure. Close the open end of the bag and place pot and bag into the centre of the cooker. When using two plastic bags, one inside the other, temperatures can increase up to 20 °C (68 °F) over what is reached using a single bag.
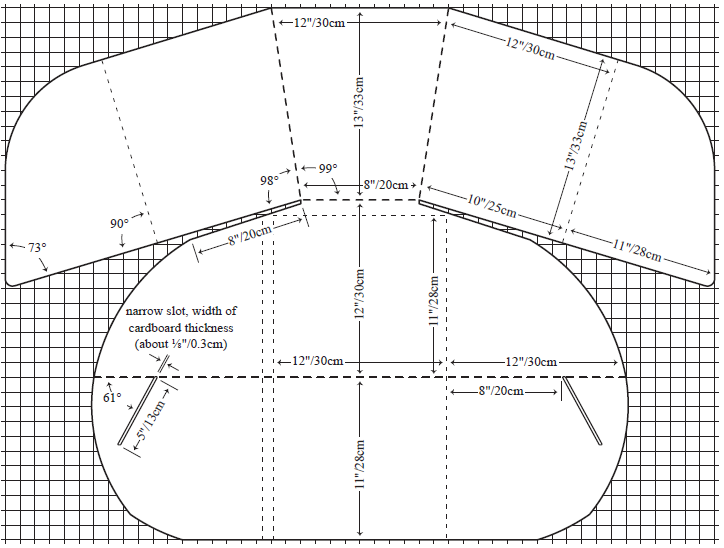
Use this link for further guidelines in making your cooker. You can experiment with different models of cookers. More efficient cookers are also a little bit more complex to build. Adapt to your purpose (experimenting, demonstrating, cooking, etc.)
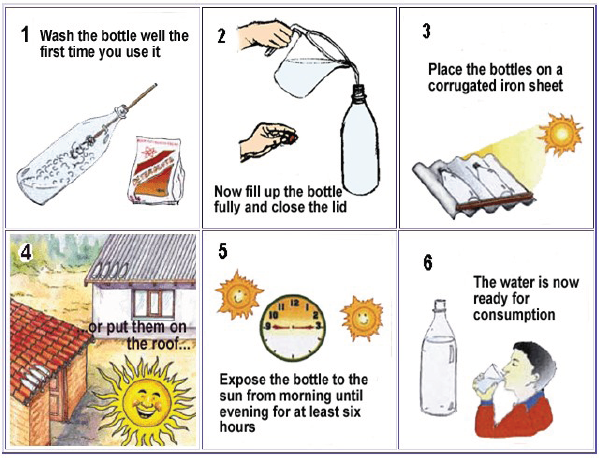
Pure water (SODIS Method)- ALL
- Wash your bottle (transparent PET or glass) if you are using it for the first time.
- Fill it with water from a natural resource such as a pond in the clean bottle. If the water is not clear let it rest for some time. When the particles in the water have settled down as sediment, use the clear water above the sediment.
- Put the bottle with water in direct sunlight for six hours during daytime.
- Now your water is perfectly purified and can be used as drinking water.
Collect water – S, VS/R
- Dig a hole of approximately 30 cm (12 inches) deep and 60 cm (24 inches) in diameter in the ground.
- Collect any fresh green vegetation from the nearby area and fill the hole with them. Weeds and/or lawn clippings are ideal in a suburban environment.
- Place the jar in the centre of the hole and make sure it has a firm foundation, i.e. it is resting on the ground and not on the vegetation.
- Cover the hole with a clear plastic sheet. Any coloured plastic sheet will work, but with a clear one you can see clearly what is happening. Use the stones to weigh down the edges of the plastic sheet.
- Place the pebble in the centre of the sheet so that it makes a dip in the plastic sheet, which must be exactly above the jar in the hole.
- Let the sun shine on the plastic sheet and observe what happens.
Section D – Go Solar!
Have a solar lunch – ALL
Use the solar box cooker to make a meal for your group? Start with easy steps, like melting chocolate or boiling water for tea/coffee, and then try more complex recipes. Basics like rice are easy for beginners.
Use clean water – ALL
Now that you have learned how to purify water for drinking using the SODIS method, figure out:
- how much water your family uses to drink, cook, and brush your teeth.
- how many bottles you will need to have to use the SODIS method to purify enough water for your family to use every day.
- how much space all of these bottles will take up if you had to place them out in the sun.
Compare your answers with other members of your group.
Advanced – Investigate other ways to purify water for drinking using the sun that might be easier for your family to use.
“Go Solar” Energy Campaign – VS/R
Work with other members of your Unit or Crew to highlight the amount of solar energy that Trinidad and Tobago receives annually and how we can use solar energy to reduce our carbon footprint as a nation. Your campaign can be in the form of coordinated social media posts that raise awareness of the issue and how each person can “Go Solar”. You can also research the cost of solar energy and show what it would take for a family to convert to solar energy. Please get permission from your parent or guardian before posting to social media and include the following hashtags on your posts #ScoutsTTgoesSolar #ScoutsTT #EarthTribe
Hot water for a bath – S, VS/R)
Save electricity by making your very own solar water heater. This will give you enough warm water for a bath for one person and can be useful when you are camping without electricity.
What you need – A black or dark coloured 5-gallon bucket, foil paper or a large black garbage bag.
Method – On a sunny dat, fill the bucket with water leaving about an inch or two from the surface to prevent spillage. Place it in a location that gets a lot of direct afternoon sunshine. Then either cover the top of the bucket with foil paper or place it inside a garbage bag and tie the bag shut. Leave it alone until sunset. Now you should have a bucket of warm water to use for a nice warm bath. (test the water to make sure that it’s not too hot to bathe with before using it)
Further work – Test to see how long after sunset the water in the bucket remains warm.
Solar Energy Resources
The material for this badge was adapted from the World Organisation of the Scout Movement (WOSM)’s activity manual for the Scouts Go Solar Earth Tribe badge which can be found here – https://www.scout.org/es/ScoutsGoSolar-manual.
You are encouraged to research further to gain even more knowledge in this diverse source of energy.
Solar Videos:
Feel free to look at the sources below to begin learning about solar energy.
- Solar Power 101
- What is Solar Energy?
- Invention of the Solar House
- Solar Energy for Kids
- The Power of Sunlight
- How Does Solar Energy Work?
- The Rise of Solar Power
Facebook References
1. Solar Bottle Lights
Create natural sources of light in dark spaces without the extreme heat. This process utilizes a 2L bottle, a solid sheet, some water, some chlorine and a box
2. Solar Drawings
Using the sun rays and a magnifying glass as well as a board, create a drawing, write your name, send a message etc..
3. Target practice
Using a mirror and a target, try to melt the piece of string by aiming at the target, the 1st person to do so gets the prize
